(Inked-Pixels/Shutterestock)
The nation’s electrical grids are extra weak to blackouts than they was once. Whether or not it’s cyber criminals hacking into the grid or the shift to renewable power sources, electrical energy distribution is at a vital juncture proper now. That’s why a latest venture on the Nationwide Renewable Power Laboratory (NREL) that demonstrated how a brand new supply real-time electrical grid information–from cable tv networks, of all locations–provides new hope to grid operators that reliability will be maintained.
Threats to the nation’s infrastructure, together with the electrical grids, have been on the rise lately. Ransomware introduced down a key East Coast gasoline supply pipeline in 2021, whereas in 2022, a safety researcher demonstrated a hack of a wise app developed by Jacuzzi, giving him management over 1000’s of spas. Extra lately, vandals geared up with rifles and shotguns have destroyed gear at electrical substations. The shift to carbon-free power era, in addition to electrical car (EV) mandates, provides additional stress to the grids (extra on that in a minute).
Getting higher and sooner perception into potential issues occurring on the grid has grow to be a nationwide precedence in Washington D.C. In 2019, the Nationwide Renewable Power Laboratory (NREL) started the Situational Consciousness of Grid Anomalies (SAGA) venture. The three-year, $3 million venture was funded by the Division of Power’s Workplace of Cybersecurity, Power Safety, and Emergency Response commenced, and would search to supply real-time info on the state of the grid.
The crystalizing second for the lately accomplished venture was the belief that the last-mile supply of the electrical grid “is basically blind,” says Scott Caruso, who heads up strategic ventures for CableLabs and who spearheaded the SAGA venture.
“For all of the discuss of sensors and Industrial Web of Issues (IIoT), there’s a definite lack of visibility into the standing of energy availability and high quality within the final miles of {the electrical} distribution grid,” Caruso wrote again in 2019.
Nevertheless, it additionally occurs to be true that {the electrical} grid coexists with cable TV and broadband gear. In reality, cable and broadband strains are related to about 95% of properties within the U.S., and 97% of them have cable inside 1,000 toes.
“That’s sort of the ‘aha’ [moment],” Caruso tells Datanami in a latest interview. “They share the identical poles. They’re in the identical trenches. They’re actually facet by facet.
What if that cable TV and broadband infrastructure could possibly be tapped to find out the state of the grid gear that it’s related to? That’s what the SAGA venture explored, and that’s what was finally delivered in a product referred to as Energy Occasion Notification System (PENS) from Gridmetrics, CableLabs’ for-profit arm.
Earlier than the SAGA venture or PENS, there was no communications happening between these two networks, Caruso says. The communication firms have been working all sorts of gear that required electrical energy from the grid, together with Wi-Fi hotspots, 5G small cell in the direction of, or broadband fiber optic nodes, however the energy (and information) flowed in only one path.
“Properly, it seems these gadgets are actually commercial-grade, subtle UPSs,” Caruso says. “In addition they have a cable modem inside them. Our information comes from these gadgets. That’s the place all of these items began. And in combination, right now we now have lots of of 1000’s of these. So if you sort of step again and take a look at it, what you actually have is that this first-time ever, unbiased, holistic view of the ability grid.”
Earlier than SAGA, the communications suppliers polled their energy provides at most 10 instances per day. That meant about 2.5 hours might go by between a verify on the community–not very helpful. Underneath the SAGA venture, that polling was bumped as much as as soon as each 5 minutes, by way of Easy Community Monitoring Protocol (SNMP). “It sounds prefer it’s trivial, however it’s a large raise,” Caruso says.
Now voltage readings have been being collected from lots of of 1000’s of factors on the grid each 5 minutes, which resulted in terabytes price of knowledge, Caruso says. Armed with two years’ price of this information, the researchers at NREL, CableLabs, and the College of Colorado created a database of anticipated values. If any of the sensors returned a real-time worth that deviated from the anticipated worth, it might be flagged as anomalous habits that might point out a cybersecurity occasion or different trigger for concern.
Further work was performed to hyperlink the sensors to vital items of infrastructure, reminiscent of energy vegetation, water reservoir, hydropower techniques, or airports, Caruso says. “What we developed was the flexibility to group the sensors after which search for occasions that have been associated to that sort of asset, if you’ll,” he says.
Immediately, grid operators had a a lot clearer and up-to-date view of the grid and the place outages have been occurring. Utilities now not needed to depend on clients to name in and complain a few energy outage, or scan Twitter for related complaints. It might know by merely monitoring Gridmetrics’ PENS product and its intuitive GUI.
What’s extra, PENS supplied a God-like view of grid habits–and doable cyberattacks–that cross utility boundaries. The U.S. energy grid consists of three,200 distinct entities, Caruso says, however with grid-level information coming from communications gear, the cyber entity using a safety vulnerability (such because the one found in Jacuzzi gear) to govern energy demand will be detected.
“Take it from a sizzling tub to someone who does a thermostat hack, or sooner or later, EV charging or warmth pumps,” Caruso says. “Any one in every of our utilities would by no means have the ability to understand that that was really a coordinated assault. They wouldn’t see the sample of habits.”
That’s how the SAGA venture proceeded by its first two years. Then, the venture objectives pivoted a bit. As a substitute of polling the communications gear as soon as each 5 minutes, what if information could possibly be streamed on a steady foundation?
“The very first thing was all of the work we did about creating the sort of visibility into the ability grid and getting occasions after which in search of anomalies,” Caruso says. “One of many issues that got here out of that’s, gosh, if we might have real-time streaming information and do that very same sort of evaluation, it’s a gamechanger. That fully disrupts the paradigm.”
If polling each 5 minutes was adequate for detecting cyberattacks or outages, what would a steady stream of knowledge present? Higher balancing of energy provide and demand in a dramatically altered grid, is the reply.
The electrical grid is present process an enormous transformation in the intervening time. On the one hand, utilities are transferring to decarbonize their electrical energy era by turning off coal and natura gas-burning vegetation to transferring to photo voltaic, wind, and hydro energy (states like California are additionally turning off nuclear energy).
On the identical time, the federal authorities and a few state governments are mandating a shift to electrical automobiles, which would require rather more power to circulation thorugh grids. Some states are additionally transferring to outlaw using fuel stoves, placing much more pressure on electrical energy provides.
Working a grid within the midst of those big modifications in electrical energy provide and demand would require rather more information, Caruso says.
“Immediately’s grid was architected, constructed, designed, and managed for one-way energy flows,” he says. “Abruptly, transfer era over to the sting. We all know from the [communications] world, as quickly as you progress something to the sting, you’ve acquired to have the ability to management it and handle it. That requires some stage of visibility and understanding about what’s occurring down within the distribution grid, the place there essentially is a blind spot right now.”
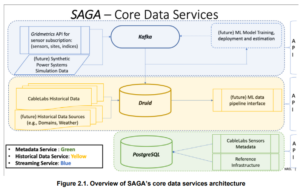
Getting real-time visibility into the grid required a totally totally different assortment of expertise. In response to the paper revealed by CableLabs and NREL, the researchers created a system that used Apache Kafka to deal with the streaming information and Apache Druid to combination the fast-moving information. The GridMetrics software program supplied visualizations and analytics on giant quantities of time-series information.
What began as a venture to spice up cybersecurity took a flip, and SAGA ended with a give attention to grid reliability. All instructed, it was a profitable product, one which now supplies a foundation for GridMetrics business software program, based on Caruso.
“We began as a mechanism for observing energy within the context of grid cyber occasions,” he says. “The place we’ve ended up is a paradigm for the place we will really allow the true time, all-the-time observability of the ability grid. It has an utility to grid cybersecurity, completely. But it surely additionally has an utility in grid operations. And that’s sort of the trajectory we’re headed now.”
Associated Gadgets:
Duke Power, GE Faucet AWS to Assist Stability the Inexperienced Grid of the Future
MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab Tackles Energy Grid Failures with AI
Can Digital Twins Assist Modernize Electrical Grids?